Model merging conflicts occur when different stakeholders aim to integrate their contradicting changes that are applied concurrently to update software models.
We conduct an extensive systematic mapping study on conflict management techniques and relevant collaboration attributes to the versioning and merging models from 2001 to the middle of 2021. This study follows the standard guidelines within the software engineering domain.
We analyzed a total of 105 articles extracted from an initial pool of more than 1800 articles to infer a taxonomy for conflict management techniques.
View on Springer
To have an integrated yet consistent merged model, conflicts have to be resolved. To this end, automation is currently at its limit or is not supported at all, and user interaction is often required.
To alleviate this flaw, there is an opportunity to apply Artificial Intelligence techniques in a collaborative modeling environment to empower the provisioning of automated and intelligent decision-making.
In this paper, we propose the use of reinforcement learning algorithms to achieve merging conflict resolution with a high degree of automation. This enables the personalized and quality-based integration of model versions.
View on Science Direct
Business Intelligence (BI) helps organizations in making data-driven decisions by visualizing the current and historical data. Despite the plethora of BI tools, their accessibility and usability are still issues.
To alleviate these issues, organizations use Chatbots. However, due to the variety of requirements and different organizational structures, developing a BI chatbot is a complex task that requires the collaboration of technical and BI experts.
In this paper, we propose a model-driven approach for the automatic generation of personalized BI chatbots for organizations.
View on IEEE
This paper presents a formalism to facilitate the specification of the logic behind merging N concurrent versions.
The proposed formalism can be used in different merging scenarios to help domain experts analyze their integration requirements more precisely.
We introduced three types of merging rules to empower our formalism for specifying all possible scenarios in merging N model versions.
View on IEEE
Model-Driven Engineering uses model transformations to propagate changes between source and target models. In some development scenarios, target models should be updated based on the evolution of source models.
In such cases, it is required to re-execute all transformation rules to update the target model. Incremental execution of transformations, which partially executes the transformation rules, is a solution to this problem.
The Epsilon Transformation Language (ETL) is a well-known model transformation language that does not support incremental executions. In this paper, we propose an approach to support the incremental execution of ETL transformations.
View on VSE Scientific Journals
When dealing with complex systems, teams of stakeholders with complementary expertise work concurrently on models to produce a coherent and complete system.
In such cases, multi-user modeling environments would help designers create and refine models from multiple points of view. Such environments must be adaptable to the needs and interests of stakeholders.
To address this requirement, we propose an approach for personalized change propagation in collaborative multi-view modeling.
View on IEEE
In recent years, the number of smartphone users has increased dramatically. Due to the significant demand for mobile apps, developers often seek faster development methods and more effective tools and techniques to generate these apps.
Many of these apps are location-based apps in which users receive services based on their geographical location. In this paper, we propose a model-driven approach for the automatic generation of Android location-based mobile apps. Our framework, called ALBA, consists of a domain-specific modeling language,
a modeling tool, and a plugin which includes model to code transformations. The modeling tool enables a novice designer to model a location-based app. The model is validated against the predefined constraints and the editor prevents creating invalid models. The designer uses the plugin to generate the Android code of the app.
View on Springer
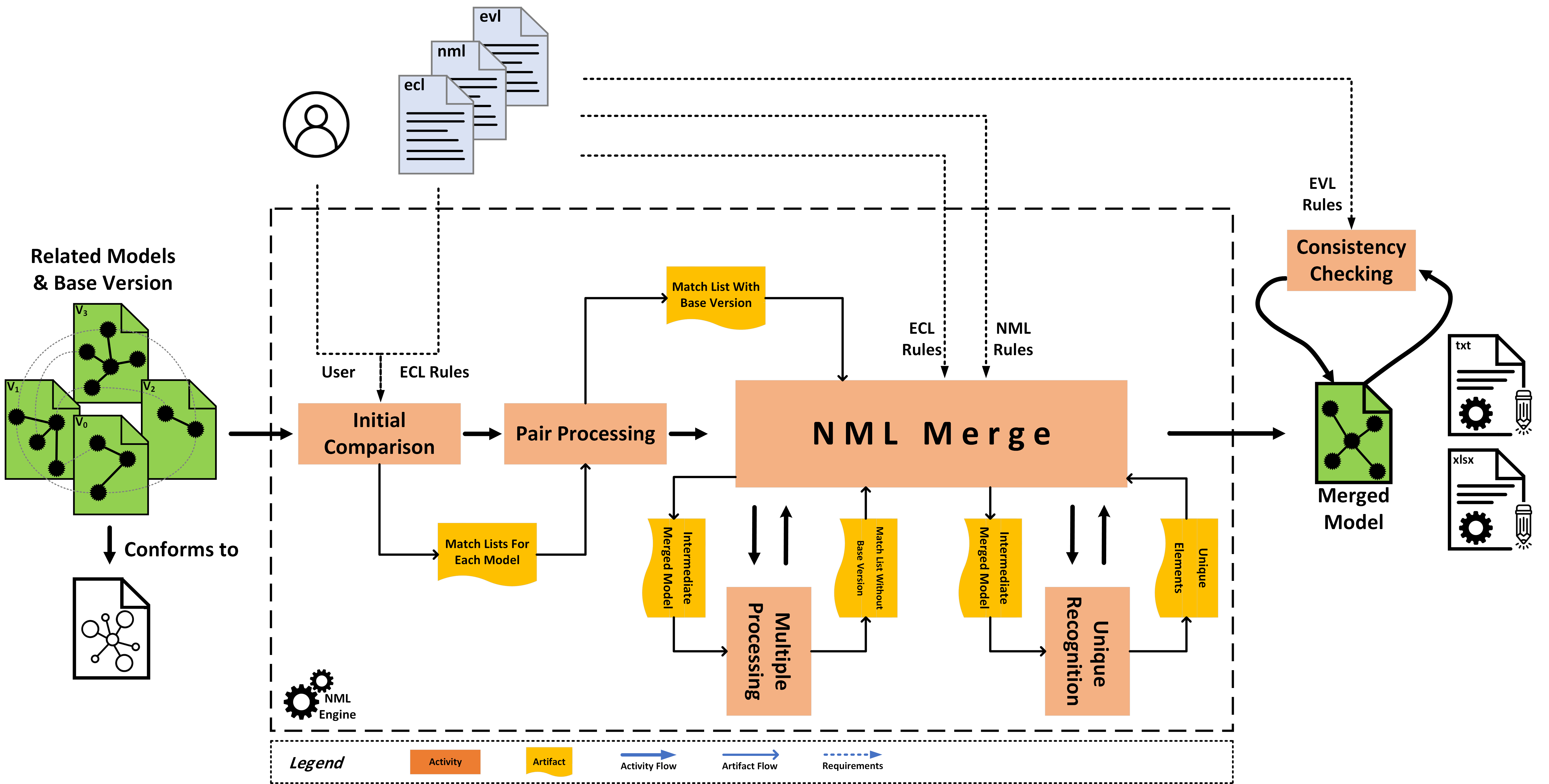
Verifying the consistency of model merging is an important step towards the support for team collaboration in software modeling and evolution. Since merging conflicts are inevitable, this has triggered intensive research on conflict management in different domains. Despite these efforts, techniques for high-level conflict representation have hardly been investigated yet.
In this paper, we propose an approach to specify model merging conflicts. This approach includes the Conflict Pattern Language (CPL), a formalism for specifying conflicts in different modeling languages. CPL is based on the OCL grammar and is tooled by an editor and a parser. CPL facilitates the slow and error-prone task of specifying model merging conflicts and can be used to specify conflicts in any EMF-based model.
View on Springer
The quality of model transformations (MT) has high impact on model-driven engineering (MDE) software development approaches, because of the central role played by transformations in MDE for refining, migrating, refactoring and other operations on models.
For programming languages, a popular paradigm for code quality is the concept of technical debt (TD). Whilst the analysis and management of quality flaws and TD in programming languages has been investigated in depth over several years, less research on the topic has been carried out for model transformations.
In this paper we investigate the characteristics of quality flaws and technical debt in model transformation languages, based upon systematic analysis of over 100 transformation cases in four leading MT languages. Based on quality flaw indicators for TD, we identify significant differences in the level and kinds of technical debt in different MT languages, and we propose ways in which TD in MT can be reduced and managed.
View on Science Direct
Software development is a collaborative activity that requires teams of software engineers to cooperate and work in parallel on versions of models. However, model management techniques such as model differencing, merging,
and versioning have turned out to be difficult challenges, due to the complexity of operations and graph‐like nature of models. This paper presents a novel process for model merging, called the Epsilon‐based Three‐way Merging Process (E3MP) process.
E3MP includes three components implemented into the Epsilon framework. First, modelers can define domain‐specific rules that customize the merging process. Second, E3MP enables an automated method for syntactic and semantic conflict detection amongst different versions of the system model. Third, E3MP puts forward a pattern‐based approach for conflict resolution.
View on Wiley
Agile and Model-Driven Development integration (Agile MDD) is of significant interest to researchers who want to leverage the best of both worlds. Currently, there is no clear evidence or proof for
the real impact of such integration. As a first step in this direction, this paper reports an empirical investigation on the impact of integrating Agile and Model-Driven Development on the quality of software systems.
View on Springer
Model transformations (MT), as with any other software artifact, may contain quality flaws. Even if a transformation is functionally correct, such flaws will impair maintenance
activities such as enhancement and porting. The concept of technical debt (TD) models the impact of such flaws as a burden carried by the software which must either be settled in a ‘lump sum’ to eradicate the flaw,
or paid in the ongoing additional costs of maintaining the software with the flaw. In this paper we investigate the characteristics of technical debt in model transformations, analysing a range of MT cases in different
MT languages, and using measures of quality flaws or ‘bad smells’ for MT, adapted from code measures. Based on these measures we identify significant differences in the level and kinds of technical debt in different MT languages, and we propose ways in which TD can be reduced.
View on Springer
Model transformation design patterns have been proposed by a number of researchers, but their usage appears to be sporadic and sometimes patterns are applied without recognition of the pattern. In this paper we provide a systematic literature review of transformation design pattern applications.
Find out more
For some conflict detection approaches in model versioning, it is required to describe conflict constraints which are an open issue. In contribution to the solution of this problem, we present a UML profile for modeling conflict conditions which can be used for automatic generation of required constraints.
View on IEEE
More on Google Scholar